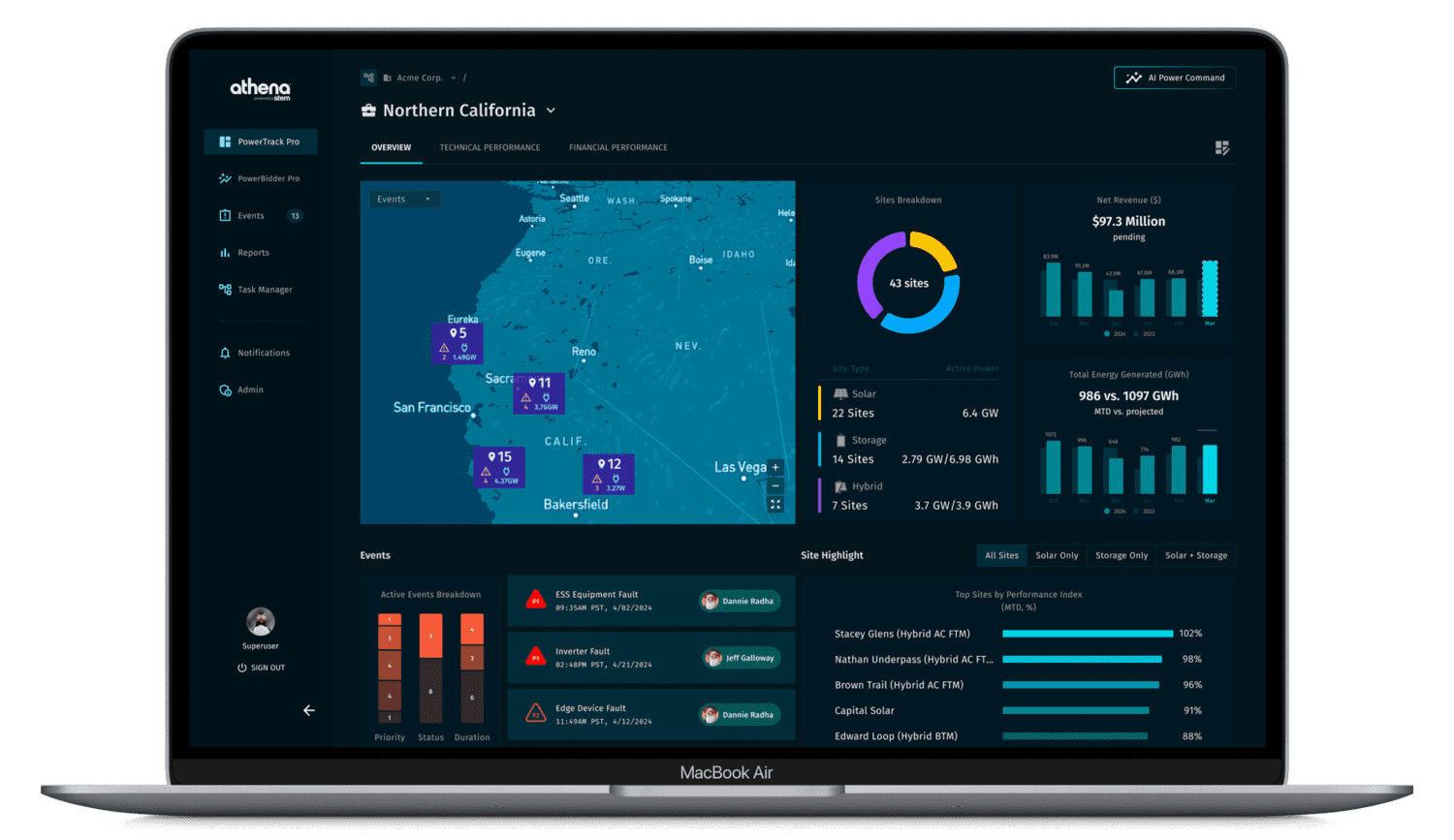
Empowering Asset Owners and Operators to Maximize Performance
One solution for gigawatt-scale storage and solar portfolios with PowerTrack™ Asset Performance Management
Stem is a Global Leader in AI-driven Clean Energy Solutions and Services
We offer integrated solutions to improve returns and maximize the economic, environmental, and resiliency value across energy assets for solar and battery energy storage.

Play Video
Buy Leading Stem and AlsoEnergy Products
We make it easy to get a quote and purchase from your preferred distributor.
Standalone Storage
Solar and Storage
Solar Monitoring Bundle
Order via AlsoEnergy.com
Storage and EV Charging Management Bundle
Solar, Storage, and EV Charging Management
Athena®
The enterprise platform that unlocks flexibility
across the clean energy value chain
Learn how you can confidently deploy and monetize clean energy technologies at scale through an extensible platform.

Benchmarking ERCOT Performance of Stem’s Athena®️ Optimization Platform
Read how Athena can improve the revenue of energy storage assets in ERCOT by an average of 28%.
Stem is trusted by industry leading project developers, asset owners, utilities, and energy traders


















Become an energy optimization expert with Stem University
Our leading training platform helps you learn how to sell, model, integrate, and deploy energy storage projects with our Athena platform in the top U.S. energy markets.

Our customers are standardizing on Stem to simplify their clean energy management
See how our customers have achieved success with Stem’s exceptional service backed by the industry’s best software.